
Today, February 4, marks World Cancer Day, a day set aside to raise awareness about cancer, encourage early detection, and support those affected by the disease. Despite advances in medicine, cancer is still surrounded by fear, rumors, and misconceptions that make people anxious or even stop them from seeking help.
From claims that cancer is contagious to fears about everyday items causing it, myths spread faster than facts. Knowing the truth can save lives. Today, let’s look at some of the most common cancer myths, uncover the truths behind them, and understand why awareness matters.
1. Cancer is a Death Sentence
One of the strongest fears people have is that a cancer diagnosis means the end. It’s easy to see why this myth persists. Many still hear stories of late-stage diagnoses that ended in tragedy. The truth is far from this fatalistic view.
Thanks to modern medicine, many cancers are treatable, especially when detected early. Survival rates for common cancers like breast, thyroid, and prostate have improved significantly. A diagnosis is serious, yes, but it does not automatically mean death. Early check-ups, treatment, and lifestyle choices can all make a real difference.
Understanding the seriousness of cancer is important, but so is knowing it cannot spread like the flu.
Read: Debunking Common Breast Cancer Myths
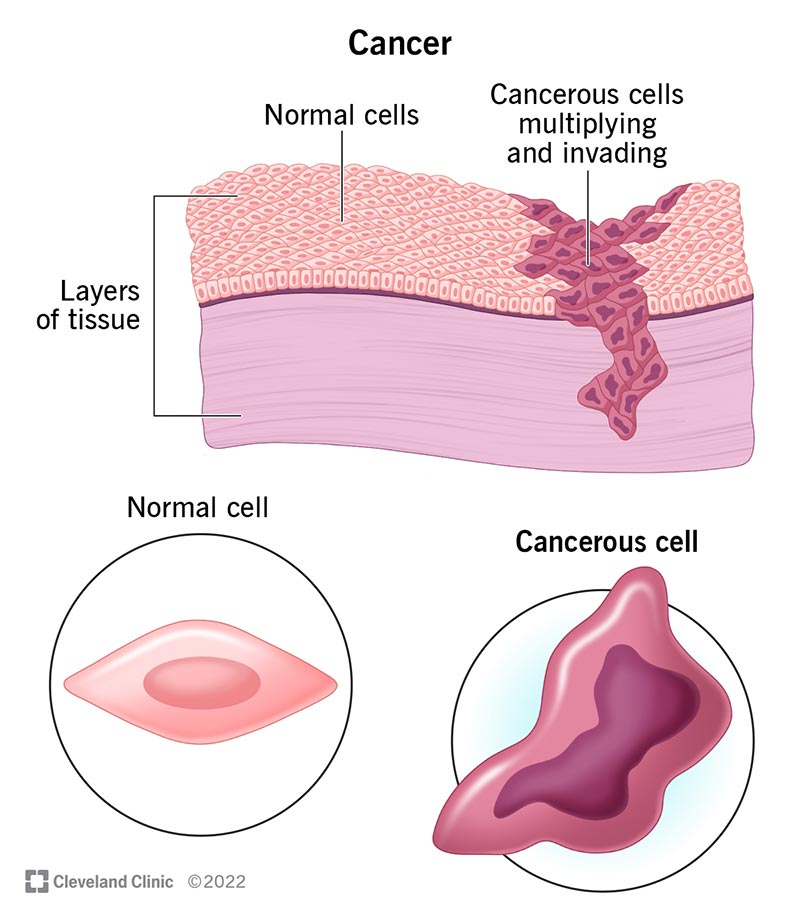
2. It is Contagious
Some people worry they could “catch” cancer from someone else, but this is completely false.
Cancer is a disease of the body’s cells, caused by genetic mutations and environmental factors, not germs or viruses that spread through touch or close contact. Even lung or skin cancers cannot be transmitted from person to person. While some viruses like HPV can increase cancer risk, the cancer itself is not contagious. Knowing this fact helps reduce the stigma that isolates patients and allows friends and family to offer real support without fear.
If myths about spreading cancer are false, what about fears surrounding our daily habits?
3. Everyday Items Cause Cancer
Many people worry that microwaves, cellphones, deodorants, or underwire bras can give them cancer. These fears are common, but none have solid scientific proof. Cellphones emit low-frequency energy, microwaves contain radiation that stays inside the oven, and deodorants or underwire bras have not been shown to increase cancer risk. Even drinking from plastic bottles left in the sun does not cause cancer.
While it’s smart to use items safely and reasonably, fixating on them distracts from the real risk factors like smoking, poor diet, inactivity, or exposure to harmful chemicals. Focus on habits that matter rather than harmless daily routines.
Speaking of habits, another persistent myth involves sugar and diet.
4. Sugar, Sweeteners, and Diet Alone Cause or Cure Cancer
Many people believe cutting sugar or avoiding artificial sweeteners can prevent or cure cancer. The reality is more balanced. Sugar does not feed cancer directly, and sweeteners approved for human use are not linked to cancer. What matters is overall lifestyle.
Excess sugar can contribute to obesity, which may increase cancer risk, but removing it entirely won’t eliminate the disease. Eating a healthy diet, staying active, and keeping a reasonable weight support your body’s health and can reduce risk, but diet alone cannot cure cancer. Moderation, not fear, is the key.
Cancer is often thought of as an older person’s disease, but that isn’t the full story.
Read: Can Suya Cause Cancer? Here’s What Doctors Are Saying
5. Only Older People Get Cancer
It’s true that age increases cancer risk, but young people and even children can develop it. Leukemia, brain tumors, and certain lymphomas are examples that often affect younger populations. Lifestyle factors, such as smoking, alcohol, obesity, and sun exposure, also play a role at any age. Recognizing that cancer can affect anyone emphasizes the importance of healthy living, awareness, and regular check-ups, no matter how old or young you are.
Finally, some people put their trust in unproven remedies.
6. Alternative Therapies Can Cure Cancer
From herbal remedies to urine therapy, some claims promise a cure without medical treatment. These are dangerous myths. Evidence-based treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapies save lives.
Relying only on unproven remedies can delay care and reduce survival chances. Always consult qualified healthcare professionals and follow proven treatment plans to maximize outcomes. Supportive therapies can complement treatment but should never replace it.
Information is Power, When It’s Accurate
Dispelling myths about cancer is a step toward prevention, early detection, and compassion. Understanding the facts helps reduce fear and stigma, empowers people to make healthier choices, and encourages timely medical care.
This World Cancer Day, check in on your loved ones, get screened if you can, and share accurate information. For more trusted guidance, resources, and support, visit RefinedNG and stay informed, healthy, and empowered.
